Configuring a per-site WAF policy with IP address restriction rules: Part one
by Hitesh Vadgama, Solutions Architect, Rackspace Technology
Introduction
I recently worked with a client who had multiple public-facing Internet Information Services (IIS) websites hosted on an Azure® virtual machine (VM). The client wanted to restrict inbound internet access to one specific website by specifying a set of allowed external IP addresses and leave the traffic flow for the other websites unaffected.
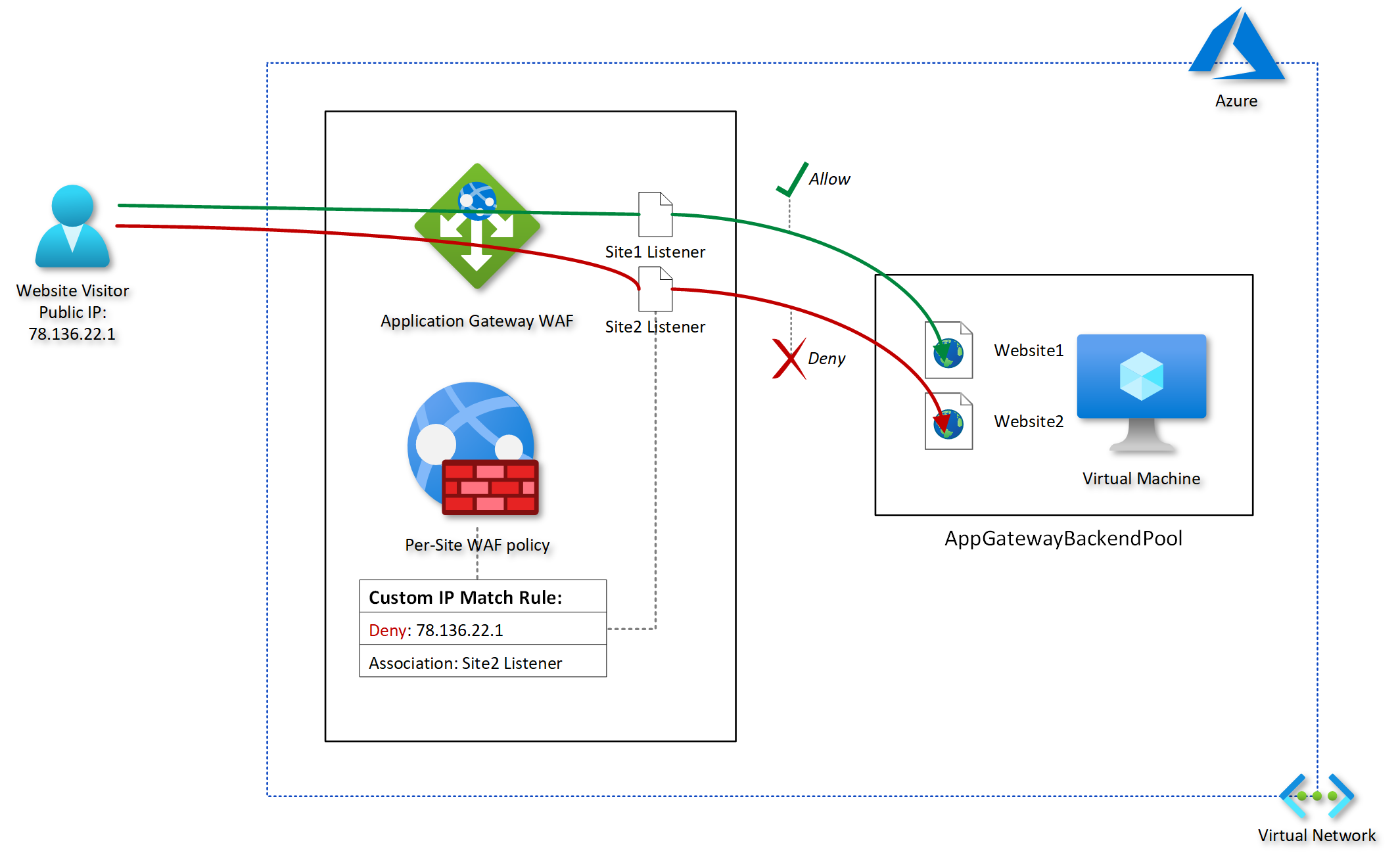
A common approach to achieve this is to use an Application Gateway web application firewall (WAF) in front of the target VM. Then, create a per-site WAF policy with an IP-based access control rule and assign it to the Application Gateway and the listener that corresponds to
the particular website’s hostname.
An IP–based access control rule is a custom WAF rule that lets you control access to your web applications. It does this by specifying a list of IP addresses or IP address ranges in Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) format
By assigning WAF policies to a listener, you can configure WAF settings for individual sites without the changes affecting every site. The most specific policy takes precedence. Suppose there is a global policy and a per-site policy (a WAF policy associated with a listener). In that case, the per-site policy overrides the global WAF policy for that listener. Other listeners without their own policies are affected by only the global WAF policy.
In this series of posts, I run through a simplified configuration to demonstrate how to apply a per-site WAF policy to an Application Gateway to control inbound access based on IP-based restrictions to one of two test IIS websites running on a single Windows VM.
The following diagram provides a conceptual illustration of my goal:
Implementation walkthrough
This three-post series covers the following elements of the implementation walkthrough:
- Introduction
- Assumptions
Application Gateway configuration:
- Web application firewall
- Backend pool
- HTTP settings
- Frontend IP configurations
- Listeners
- Rules
- WAF policy configuration
- Testing the custom rule
- Conclusion
Assumptions
The following items are already in place, so I won't cover the provisioning steps for these items in this walkthrough:
- A Windows; Azure VM
- IIS installed and bindings configured for two test website URLs (site1.hiteshvadgama.co.uk and site2.hiteshvadgama.co.uk)
- An Application Gateway WAF (v2)
- DNS records updated to map website domains to the public IP address of the Application Gateway
Next steps
Post 2: In this series covers the Application Gateway configuration.

Recent Posts
Amazon Bedrock AgentCore Preview: A Solutions Architect’s First Look at the New Agentic AI Platform
November 13th, 2025
My Journey of Building a Terraform AI Agent — Automating Cloud Infrastructure with AI
October 31st, 2025
Microsoft's 2025 Licensing Evolution: Transform Change into Opportunity
October 9th, 2025
7 Critical AWS Architecture Risks: How to Assess and Remediate Security Gaps
September 25th, 2025
From Data Rich to Insight Rich: A Cloud Charter for 2025
September 2nd, 2025